Having itchy, irritated eczema is bad enough, but are you now dealing with staph infections on the skin? Then this article is for you. In this post, we’ll cover the symptoms and causes of staph infections, as well as the best ways to protect your skin.
What is a Staph Infection?
Staph infections are caused by bacteria called staphylococcus. This type of germ is actually commonly found on the skin of healthy people. However, if an infection develops, it’s extremely important to treat it in order to prevent the bacteria from invading the body deeper and potentially becoming life-threatening.
If you believe you might be suffering from an eczema staph infection, please seek professional medical help immediately.
Types of Staph Infections
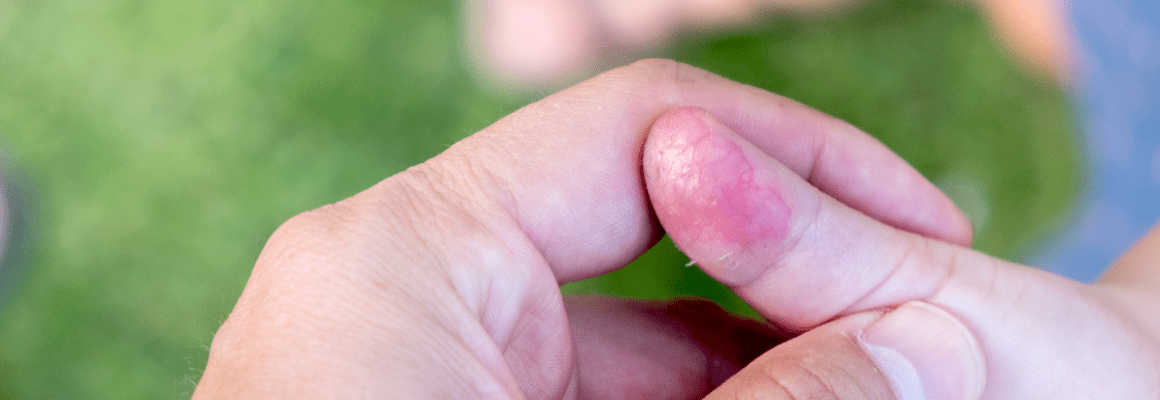
Here are the most common types of staph infections:
Furuncles: Also known as boils, this type is caused by a combination of bacteria and fungi. Typically, these boils are found on the face and neck and start growing from a hair follicle.
Impetigo: If you suffer from eczema-prone skin, this is the type of staph infection that is likely to develop. A painful and irritating wound, this type of infection causes the skin to break and weep. This makes it highly contagious, making it extra important to see a doctor.
Cellulitis: This infection is identified by tender, swollen, and red skin that’s painful to the touch. It can lead to blisters, fevers, and a fast-spreading rash. Unlike impetigo, cellulitis is not contagious. However, if left untreated, it can spread to the bloodstream and lymph nodes, making it life-threatening.
Who is at Risk?
Certain people are more at risk of developing staph infections than others. These include:
- Breastfeeding women
- Newborns
- People with cancer, especially those undergoing chemotherapy
- Those with skin damage like eczema
- Those with a weakened immune system
- People who inject drugs or medication
Symptoms of Staph Infection
The main symptoms of a staph infection include:
- Red, painful bump
- Swollen skin
- Sores and blisters
- Red eyelids
Are Staph Infections Contagious?
As mentioned earlier, the bacteria that cause staph infections live harmlessly on the skin of many people. An infection only develops if the bacteria get into the skin. This is usually through a break in the skin from a bite or cut.
This infection can then be spread to others through sharing personal items like towels or toothbrushes, close skin contact, and even though coughs and sneezes.
Protecting your Skin from Staph Infections
Here are our top tips for protecting your skin from developing a staph infection or spreading it to others:
Cover Open Wounds: Cuts, wounds, and broken skin are the perfect opening for bacteria to enter the body. In addition, pus from infected sores has a high likelihood of containing staph bacteria. We recommend you cover any open wounds with these Remedywear™ Bandages for babies to adults. Made with eco-friendly TENCEL and embedded with zinc-oxide, they’re soft and comfortable to wear and can be easily worn underneath regular clothing.
Don’t Share Personal Items: As stated earlier, it’s possible for staph infections to spread from person to person as well as on objects. To prevent this from happening, don’t share personal items such as clothing, razors, bedsheets, towels, and even athletic equipment. Washing bedding and clothing in hot water and then drying in a hot dryer can help kill the staph bacteria.
Protect Skin from Scratching: Relentless scratching can cause the skin to crack or break, paving the way for bacteria to easily enter. To reduce the risk of this occurring, it’s important to protect your skin from the vicious itch-scratch cycle so common in those suffering from eczema. A great way to do this is by wearing these Remedywear™ Gloves for adults or kids. Featuring moisture-wicking sweat control, they’re perfect for wearing all day or throughout the night when you may be scratching subconsciously.
References:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/staphylococcal-infections/