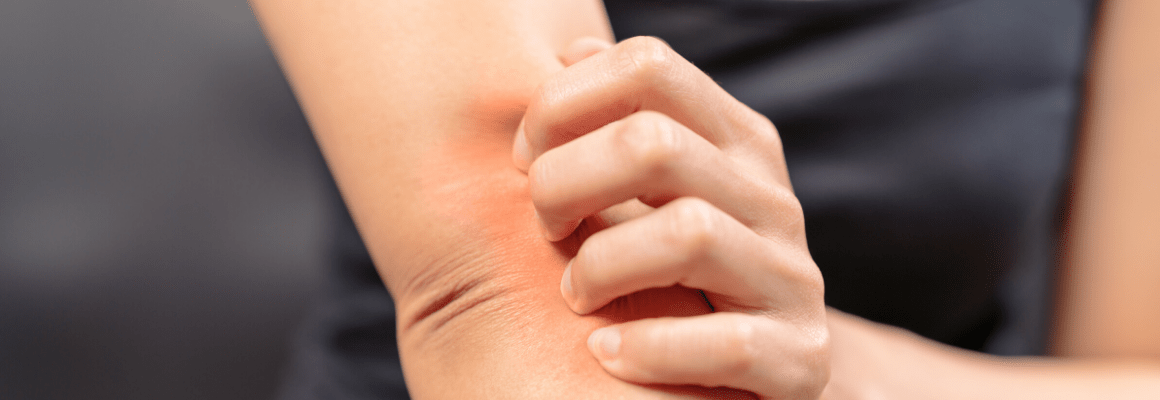
Is atopic dermatitis eczema? This is a common question many people wonder. As both refer to skin conditions, the terms are often used interchangeably. However, it’s important to understand the difference between the two. Let’s take a closer look at atopic dermatitis vs. eczema.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects over 30 million Americans. Although researchers don’t know exactly what causes it, it’s believed to develop as a result of genetic and environmental factors.
While the term is generally used to describe the condition that causes the skin to be dry, red, and inflamed, there are actually several different types of eczema. The most common types include contact dermatitis, nummular eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and, of course, atopic dermatitis. While all of these types have distinct characteristics, they all fall under the eczema umbrella and share symptoms of itchiness.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Also known as simply AD, this is the most common type of eczema, affecting as many as 18 million Americans. It usually develops in childhood, appearing as an itchy, red rash on the cheeks, arms, and legs (although it can develop in other places as well).
While AD is a chronic condition, many go through phases where symptoms flare periodically. Its primary characteristics are dry, scaly skin, redness, and itchiness.
Atopic dermatitis is linked to what is known as the atopic triad. This refers to a group of allergies that are often experienced simultaneously: asthma, hay fever and atopic dermatitis. Research suggests that those with a family history of asthma and/or hay fever, are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis as well.
Is Atopic Dermatitis Eczema?
Atopic dermatitis is considered the most common and more severe type of eczema. In addition to red, inflamed and dry skin, sufferers may also develop blisters, skin cracking, crusting, weeping, and scaling.
Atopic dermatitis can also be triggered or worsened by low humidity, cold temperatures, and exposure to allergens such as soaps and detergents. The main skin areas to be affected include the folds of the arms, the back of the knees, wrists, face, and neck.
Alternatively, the causes of eczema can vary depending on the type of eczema. In addition, the appearance and location will be different depending on the type of eczema. For example, contact dermatitis is characterized by a red rash that develops in response to direct contact with a substance in the environment while stasis dermatitis is characterized by skin inflammation that commonly occurs in the lower leg as a result of poor circulation.
Natural Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis
Stay Moisturized
To counter the drying effects of a damaged skin barrier regardless of eczema or atopic dermatitis, it’s important to stay moisturized. Keep your skin hydrated with this Organic Manuka Honey Cream. An oil-based balm, it’s highly effective at rejuvenating even the driest of skin. With handpicked all-natural ingredients - including Manuka honey! - the balm is safe to use all over your body, including the eyes and lips.
Change your Diet
The food you eat has an effect on your skin. Certain foods that are common culprits for triggering inflammation include dairy, gluten, citrus fruits, shellfish and nuts. Alternatively, anti-inflammatory foods that are known to reduce eczema symptoms include foods such as apples, blueberries, kale, broccoli and spinach.
If you don’t know what your food triggers are, we recommend trying an elimination diet. This involves removing the consumption of certain foods from your diet for a certain period of time (usually about a month) and then incorporating these foods back in.
Wear Eczema Friendly Clothing
Protect and soothe your irritated skin by wearing eczema-friendly clothing such as those from Remedywear™. Combining eco-friendly TENCEL™ with anti-bacterial zinc, the result is comfortable, breathable garments that can be worn all day or as an overnight treatment. All garments are specifically designed to combat the urge to scratch by providing a gentle layer of protection in the areas you need it most.
Here are some of our favorites:
Remedywear™ (TENCEL + Zinc) Long Sleeve Shirt - ADULT Unisex
Remedywear™ (TENCEL + Zinc) Pants - ADULT Unisex
Remedywear™ (TENCEL + Zinc) Long Sleeve Shirt for KIDS
Remedywear™ (TENCEL + Zinc) Long Pants for KIDS
References
https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/atopic-dermatitis/ https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/ https://www.medicinenet.com/atopic_dermatitis/article.htm https://www.medicinenet.com/atopic_dermatitis_vs_eczema/article.htm