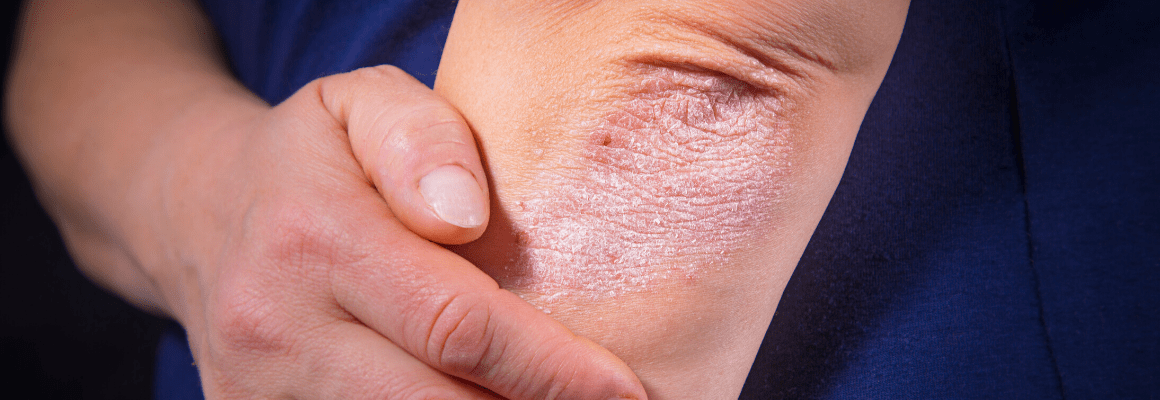
Did you know vitamin D may help your eczema? But how much is good for you and where can you get supplements if necessary? Let’s take a closer look at the relationship between the two.
Eczema and Vitamin D Deficiency
Your immune system suffers if your body is not producing enough vitamin D. A deficiency can weaken the skin barrier, causing it to break down and increasing the risk of infection. For those already suffering from a damaged skin barrier, this is undoubtedly bad news! Have you ever noticed that your eczema tends to get worse in the winter? Vitamin D deficiency is part of the reason why.
The Sun and Eczema
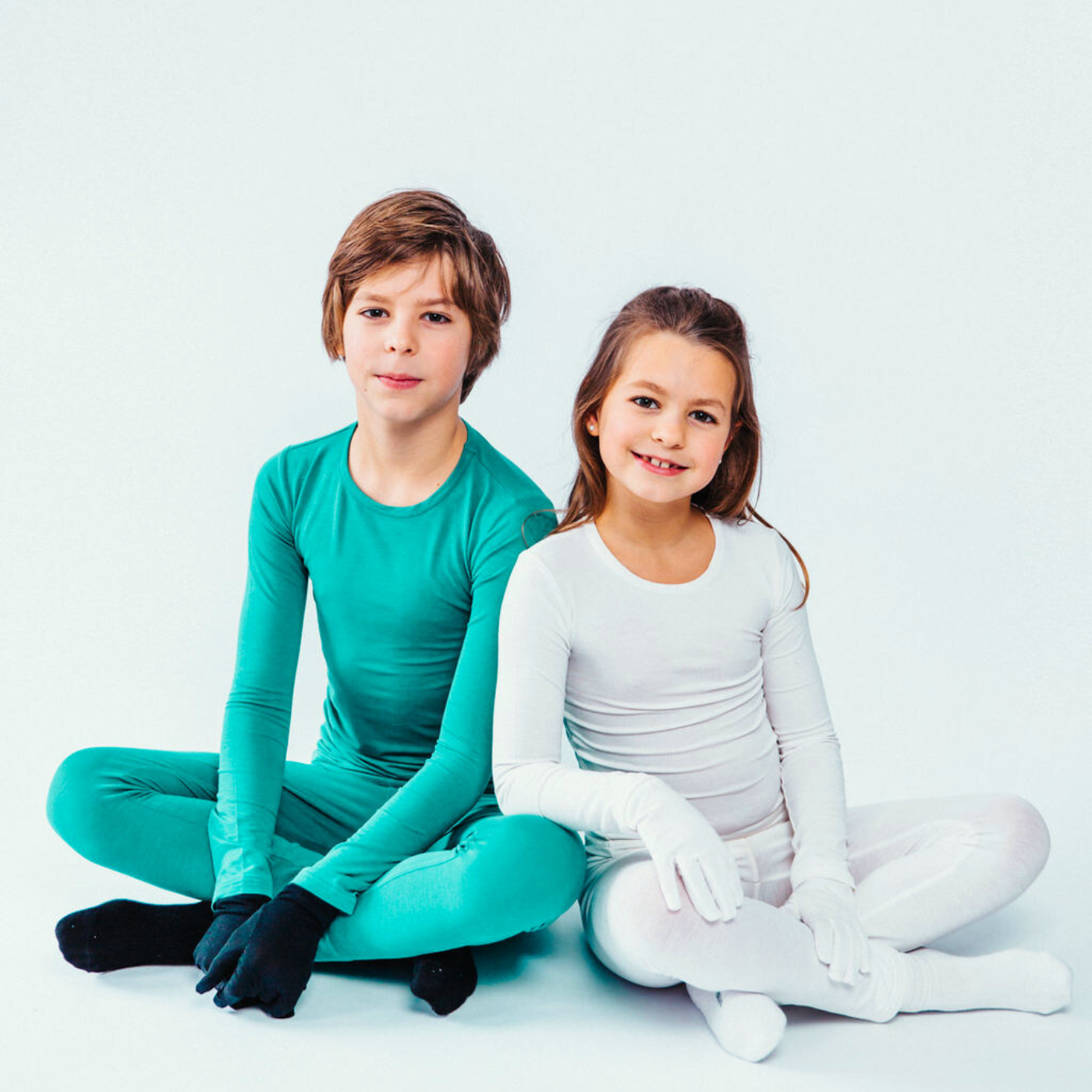
Exposure to the sun can give you that dose of Vitamin D your skin has been craving. This is because exposing your skin to light leads to increased production of vitamin D, which in turn, increases the production of a protein that fights skin infection. The trick, however, is to make sure you don't overdo it. To protect sensitive skin against flare-ups, it's recommended to be in the sun no longer than 1-2 hours at a time. You can also protect your skin from the damaging effects of UV rays by wearing special clothing that helps keep the skin cool. Our Remedywear™ clothing provides UPF 50+. The TENCEL fabric is extremely breathable to prevent the body from overheating and the moisture-wicking properties prevent sweaty irritation or uncomfortable chafing. Here are some of our favorites:
Remedywear™ Long Pants for Kids
Remedywear™ Long Pants for Adults
Remedywear™ Long Sleeve Shirt for Kids
Remedywear™ Long Sleeve Shirt for Adults
Where Can you Find Vitamin D?
One of the best ways to get vitamin D is through sunshine. Unfortunately, sunshine during the wintertime is generally in short supply. Because of this, many people expose their skin to ultraviolet light which can help stimulate the production of vitamin D in the skin. In addition, increasing your consumption of vitamin D has also proven to help treat eczema-prone skin.
Vitamin D is naturally found in fatty fish, fish oils, beef liver, egg yolks and cheese. Increasing your intake of some dairy products, orange juice, cereals, and soy milk may also help. Finally, you can also supplement vitamin D with these Viva Naturals High Potency Vitamin D3 tablets which are safe and inexpensive. Just remember to check with your doctor if you think you require a supplement with a higher dose.
How Much Should You Take?
While we know vitamin D is beneficial to the body, here’s an important question: what’s considered a healthy dose of vitamin D? How much should one take to heal safely and successfully? The answer partly depends on the season. In the summer when the sun is strong, it’s possible to generate close to 20,000 units of vitamin D from sun exposure alone. During the winter months, however, it’s unlikely that you will generate enough to meet the recommended dosage.Recommended Dosage:
| Age | Dosage |
| Below 5 | 35 units per pound per day |
| Age 5 – 10 | 2500 units |
| Adults | 4000-8000 units |
| Pregnant Women | 5000-10000 units |
Bear in mind that the only way to reliably determine exactly how much vitamin D you or your child needs is through a blood test. You should always speak to your doctor before taking any action. He or she will be able to recommend the proper supplement dosage for your condition.
Scientific Studies
Study 1: Randomized controlled trial using vitamin E and D supplementation in atopic dermatitis: In 2011, 45 eczema patients took part in an experiment to assess the effects of vitamin D and E supplementation. The study was randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. They were treated for 60 days. Both groups saw an improvement in the intensity and amount of eczema, around 35%. However, when 1600 IU of vitamin D3 and 600 IU of vitamin E were given together, patients improved by 64%. This showed that there are benefits of supplementing vitamin D for eczema patients - and that these benefits are increased when combined with vitamin E.
Study 2: Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) treated by 1600 IU of vitamin D This December 2016 study involved four randomized controlled trials. It was conducted as a systematic review in order to compile the results of previous studies on vitamin D and eczema, including the study mentioned above. From this study, they discerned that serum vitamin D levels were generally lower in eczema patients, but even more so in children. Most notably, the studies revealed that vitamin D can indeed be used to improve an eczema patient’s health and skin. Regardless of what you decide, always make sure to speak with your doctor before supplementing.
References:
Randomized controlled trial using vitamins E and D supplementation in atopic dermatitis. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) treated by 1600 IU of vitamin D